Determination of Effective Geometry
The next step in the check concerns the determination of the effective geometry of the pad foundation.
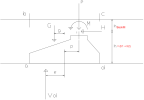
The following picture illustrates the different actions working on the foundation.
In this picture the following notations are used:
The eccentricity e is calculated as follows:
For a general 3D case this formula is written as:
Weight G
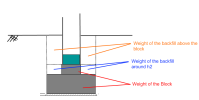
The weight G consists of three parts:
-
The weight of the foundation block, GBlock.
This depends on the shape of the block (prismatic or pyramidal), dimensions and also the density γBlock of the block material.
The density of the block depends on the Water table level.Water level Block Density No influence γBlock
at foundation base γBlock at ground level (γBlock – γw) The Water Density γw is taken as 9,81 kN/m³
-
The weight of the backfill around h2, GBackfill,Around.
This depends on the shape of the block (prismatic or pyramidal), dimensions and also the density of the backfill material.
The backfill density γBackfill,d is specified in "Determination of Design Values".
The density of the backfill depends on the Water table level.Water level Block Density No influence γBackfill,d
at foundation base γBackfill,d at ground level (γBackfill,d – γw) The Water Density γw is taken as 9,81 kN/m³
- The weight of the backfill above the foundation block, GBackfill,Above.
This depends on the height and density of the backfill as specified in the input of the Pad Foundation.
Note that the height of the backfill material can also be negative. A negative value is used to indicate that the soil is lower than the top of the foundation block.
The three parts are illustrated on the following picture:
The design value of the total weight G can then be calculated as follows:
Gd = γG * [GBlock + GBackfill,Around + GBackfill,Above]
With γG the safety factor of the permanent loading for the combination under consideration, as defined in "Determination of Design Values".
Distances gx and gy
Using the weight and the volume, the center of gravity of the block and backfill are determined. The distances gx and gy are then calculated from this centroid to the center point of the foundation base.
Effective geometry
As a final step, using the eccentricities ex and ey the effective geometry of the foundation base is calculated as follows:
L1 = A – 2 * |ex|
L2 = B – 2 * |ey|
With A & B read from the Pad Foundation library.
B’ = min (L1 ; L2)
L’ = max (L1 ; L2)
A’ = B’ * L’
In case B’ < 0 m or L’ < 0 m the geometry is incorrect.
In this case, the check is not executed and a warning is given on the output